From Laminated to Toroidal: What are the Pros and Cons of Different Transformer Cores?
Transformer cores form an essential component in electrical systems. These devices are responsible for transforming voltage and current from an input state to an output state. The ability to customize the design of transformers has led to tremendous growth in transformer systems over the years. Today, transformer cores are available in various types, ranging from the traditional laminated cores to the more advanced toroidal cores. This article will discuss the pros and cons of different transformer cores.
What is a Transformer Core?
A transformer core is a magnetic component of a transformer that conducts energy flow from one coil or circuit to the other. The core helps to distribute the magnetic flux generated by the current flowing through the transformer's primary winding throughout its secondary winding. The most commonly used materials for transformer cores include iron, steel, and laminated metals.
Laminated Cores
Laminated transformer cores are the most commonly used type of transformer core in the market. They are also the most basic type of transformer core. The core is constructed of laminated sheets of electrical steel that serve as an insulation barrier. The sheets of steel are stacked on top of each other, and they are separated by an insulating layer of paper or plastic.
Pros of Laminated Cores
Laminated cores are widely used due to their cost-effectiveness, durability, and ability to handle high voltages. These transformer cores are lightweight and take up minimal space, making them ideal for use in different applications. Laminated transformer cores also produce less noise than other transformer core types.
Cons of Laminated Cores
Laminated cores have a low saturation flux density, which limits their ability to operate under high magnetic loads. The eddy currents generated when voltage is induced, and the current flows through the transformer also increases the transformer's energy losses. This leads to lower efficiency and increased power consumption.
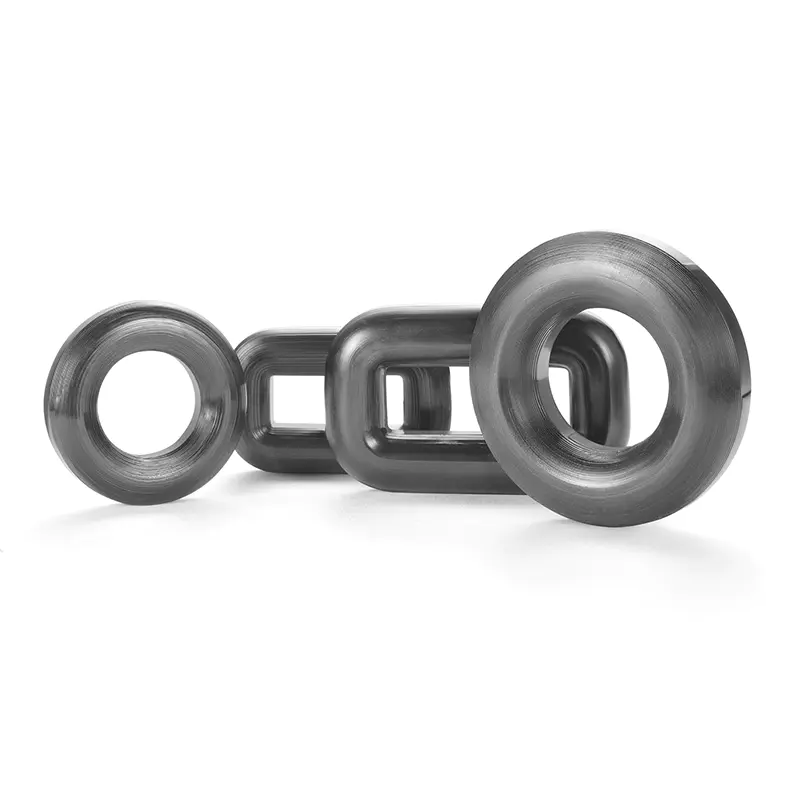
Toroidal Cores
Toroidal transformer cores are a more advanced and modern type of transformer core. The core is constructed from a circular cross-section of magnetic material and takes its name from the toroidal shape of the core.
Pros of Toroidal Cores
Toroidal cores have a higher saturation flux density than laminated cores, making them ideal for high-load applications. They also have less flux leakage and eddy current losses, leading to higher efficiency levels. The circular shape of the core also ensures that the magnetic flux is evenly distributed throughout the winding, reducing the risk of hotspots and thermal damage.
Cons of Toroidal Cores
One of the main disadvantages of toroidal cores is their higher cost compared to laminated cores. The manufacturing process involved is also more complicated, which adds to the overall cost of production. Toroidal cores are also larger and heavier than laminated cores, which can be a disadvantage in certain applications.
Ferrite Cores
Ferrite transformer cores are made of ceramic materials that are composed of iron oxide and other metal oxides. They have a high magnetic permeability, which means that they can store more energy per unit volume.
Pros of Ferrite Cores
Ferrite cores are an excellent choice for high-frequency applications due to their low losses and lightweight nature. They also have a high saturation flux density, which makes them ideal for use in high-energy applications.
Cons of Ferrite Cores
Ferrite cores have low permeability compared to other transformer cores, limiting their use in low-frequency applications. They are also brittle and prone to cracking or breaking, requiring special handling and mounting procedures to avoid damaging the core.
Amorphous transformer cores are becoming increasingly popular in the industry. They are made of thin ribbons of metal that are heated until they become fluid and cooled rapidly, resulting in a disordered or amorphous structure.
Pros of Amorphous Cores
Amorphous cores have a high magnetic permeability, which makes them ideal for use in high-precision transformer applications. They have a low core loss and high energy efficiency, even in high magnetic field applications. The manufacturing process used for amorphous cores is also eco-friendly.
Cons of Amorphous Cores
Amorphous cores are more expensive than laminated cores due to the complex manufacturing process. They are also more susceptible to damage from internal mechanical stresses, requiring special handling and mounting procedures. Finally, they do not handle high voltages well, and they are not recommended for high voltage applications.
Conclusion
In summary, selecting the right transformer core for an application requires consideration of several factors, including cost, efficiency, frequency range, size, and weight. Laminated cores, toroidal cores, ferrite cores, and amorphous cores all have their advantages and disadvantages. However, selecting the right transformer core can lead to improved performance, efficiency, and reduced power consumption.