The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using an Amorphous Cut Core for Your Transformer
Introduction
Transformers are an essential part of the electrical power distribution system. They are used to transfer energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. A transformer comprises two coils, a primary and a secondary, wound around a ferromagnetic core. The core's material and shape affect the transformer's operating characteristics such as efficiency and size. One of the core materials used is an amorphous cut core. In this article, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using an amorphous cut core for your transformer.
Definition of Amorphous Cut Core
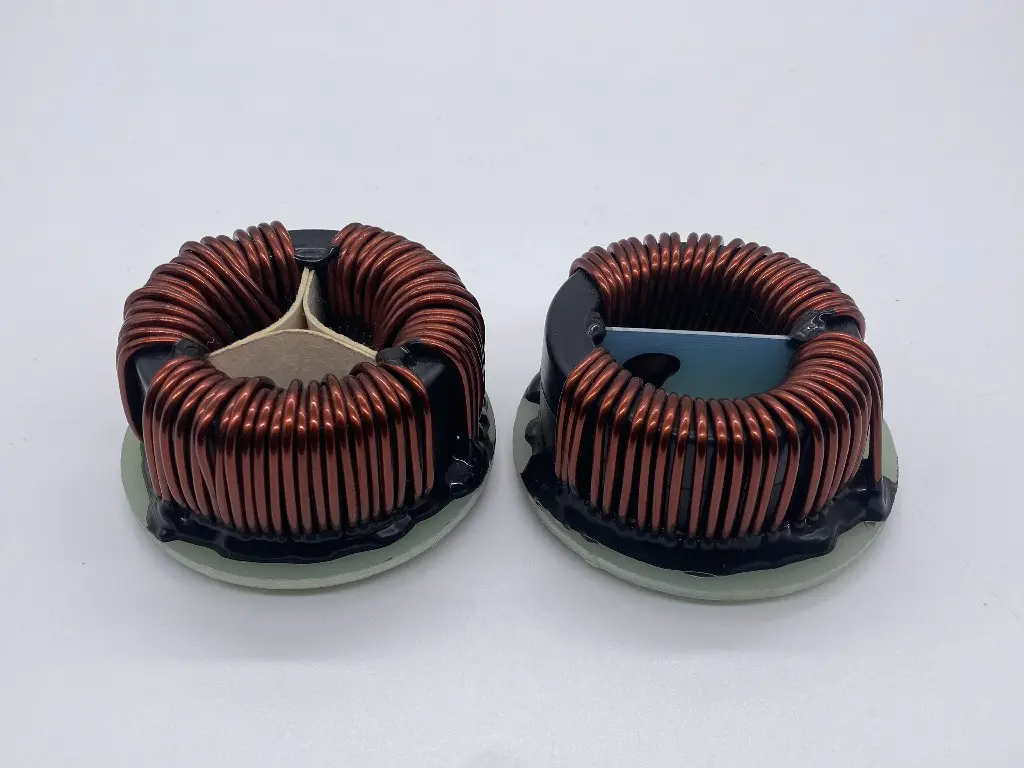
An amorphous cut core is made from a metallic glass, also known as an amorphous metal. It is a type of alloy that lacks crystalline structure, unlike conventional metals. Instead, the atoms arrange in a disordered manner, similar to glass. The amorphous metal is produced by rapidly cooling the molten alloy to create a non-crystalline solid. The amorphous cut core is then formed by slicing the amorphous metal into thin strips and stacking them into a core shape.
Advantages of Using Amorphous Cut Core
1. High Efficiency: The amorphous cut core has a magnetic permeability that is two to three times higher than that of the commonly used silicon steel. This property reduces the amount of power loss in the transformer, making it more efficient.
2. Low Core Losses: The amorphous cut core has lower magnetic core losses than a conventional silicon steel core. This property reduces the heat generated by the transformer, which leads to a longer lifespan.
3. Light Weight: The amorphous cut core is significantly lighter than the silicon steel core. This property results in smaller transformers that are easier to handle and install.
4. Quiet Operation: The amorphous cut core has lower magnetostriction, which results in quieter operation of the transformer.
5. Better Resistance to Overload: The amorphous cut core can withstand overload better than a silicon steel core. This property makes it a better choice for applications where transformers are subjected to frequent overload conditions.
Disadvantages of Using Amorphous Cut Core
1. High Cost: The amorphous cut core is more expensive than a silicon steel core. This property can make transformers with an amorphous cut core less attractive for some applications where cost is a significant factor.
2. Brittle: The amorphous cut core is more brittle than a silicon steel core. This property makes the amorphous cut core more susceptible to damage during handling and installation.
3. Limited Availability: The production of amorphous metal is not as widespread as that of silicon steel. This property can lead to longer lead times and higher costs for the amorphous cut core.
4. Sensitivity to Temperature: The amorphous cut core is more sensitive to temperature changes than a silicon steel core. This property requires special attention to the design of the transformer's cooling system to maintain its performance.
5. Lower Flux Density: The amorphous cut core has a lower flux density than a silicon steel core. This property requires more core material to achieve the same level of performance as a transformer with a silicon steel core.
Application of Amorphous Cut Core
Amorphous cut cores are used in applications where high efficiency and low core losses are critical factors. They are commonly used in high-frequency transformers, such as switch-mode power supplies for electronic devices and high-frequency welding equipment. The amorphous cut core is also used in distribution transformers for the electrical power grid, where high efficiency and low losses are essential for reducing energy waste.
Conclusion
In summary, the use of an amorphous cut core offers significant advantages, including high efficiency, low core losses, lightweight, quiet operation, and better resistance to overload. However, there are also disadvantages to using an amorphous cut core, including high cost, brittleness, limited availability, sensitivity to temperature, and lower flux density. The choice of core material depends on the application requirements, including performance, size, cost, and availability. The amorphous cut core is an excellent choice for applications that require high efficiency and low core losses, but its high cost may limit its use in some applications.