The difference between amorphous magnetic ring and ferrite core
by:Transmart
2022-12-19
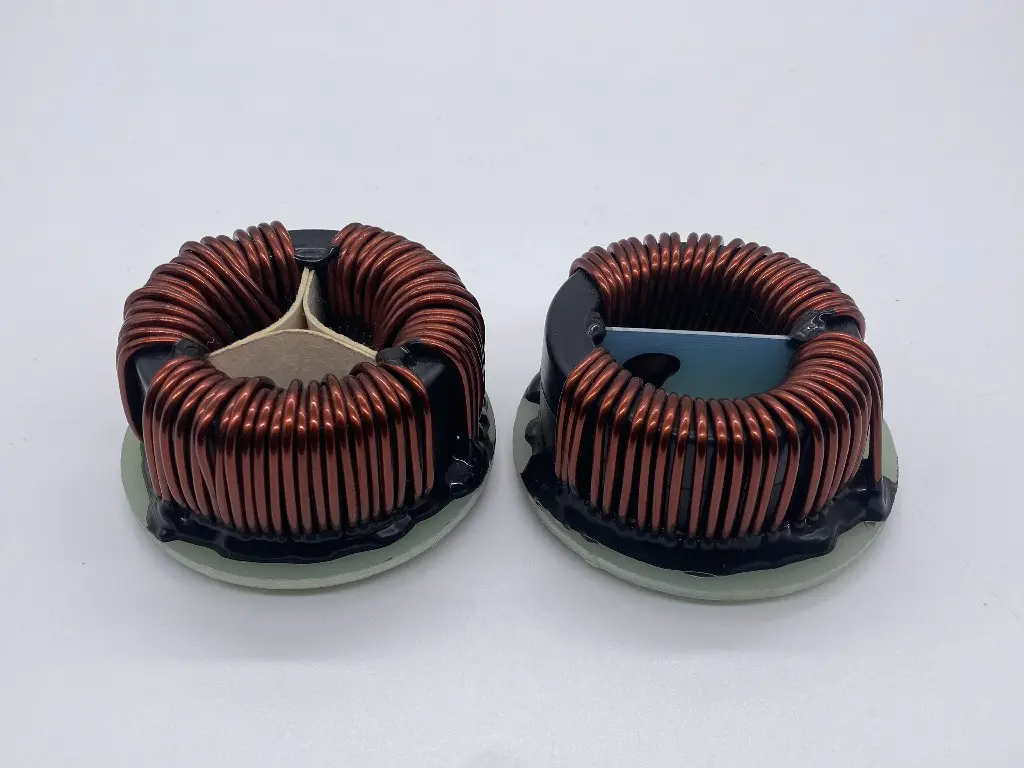
Amorphous magnetic ring is a magnetic element processed with amorphous material. According to the material of the amorphous strip used, it can be divided into iron-based amorphous, cobalt-based amorphous and so on. According to the shape of the material, it can be divided into strip type magnetic ring and powder type magnetic ring. The saturation magnetic density of the amorphous magnetic ring is much higher than that of ordinary ferrite and powder cores, but as the frequency increases, the magnetic permeability will decrease quickly, and it is generally used in the frequency band of tens of K to hundreds of K. Amorphous magnetic ring, or metallic glass, is a new type of material that came out in the 1970s. It is a solid alloy (thin strip) that is formed by using quenching technology to form a thin strip with a thickness of 30 microns at one time. ) is different from the crystal structure in which atoms are regularly arranged in cold-rolled silicon steel materials. It is this alloy whose atoms are in an amorphous structure that is randomly arranged, so that it has a narrow B-H circuit, and has the characteristics of high magnetic permeability and low loss; At the same time, the irregular atomic arrangement of amorphous alloys restricts the free passage of electrons, resulting in a resistivity 2-3 times higher than that of crystal alloys, which is also conducive to reducing eddy current losses. Compared with the traditional transformer using silicon steel sheets, the no-load loss of the transformer core made of amorphous alloy is reduced by about 75%, which makes the amorphous alloy transformer have obvious energy-saving and environmental protection effects.
Amorphous magnetic ring
Ferrite cores are mainly composed of three metal elements: iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn), and are usually called manganese-zinc ferrite. Toroidal ferrite cores have a high magnetic effect because they have no air gap and have a uniform cross-sectional area. There are many specifications and sizes of ferrite magnetic rings, which can be selected according to the different materials of the magnetic rings, and different coatings can be used to simplify winding and increase breakdown voltage. The ferrite core is made of non-metallic magnetic material with dense and homogeneous ceramic structure, and has low coercive force (after the magnetic material is saturated and magnetized, its magnetic induction intensity B does not return to zero when the external magnetic field returns to zero, Only by adding a magnetic field of a certain size in the opposite direction of the original magnetization field can the magnetic induction return to zero. This magnetic field is called the coercive field), also known as soft ferrite. It consists of iron oxide (Fe2O3) and oxide or carbonate compounds of one or several other metals (eg manganese, zinc, nickel, magnesium). The ferrite raw material is pressed, then sintered at a high temperature of 1300°C, and then machined to make a finished magnetic core that meets the application requirements. Compared with other types of magnetic materials, the advantage of ferrite is that it has a high magnetic permeability and It has the advantages of high resistance and small eddy current loss in the universal frequency range.
Custom message