The Advantages and Limitations of Using Amorphous Toroidal Cores in Transformers
The Advantages and Limitations of Using Amorphous Toroidal Cores in Transformers
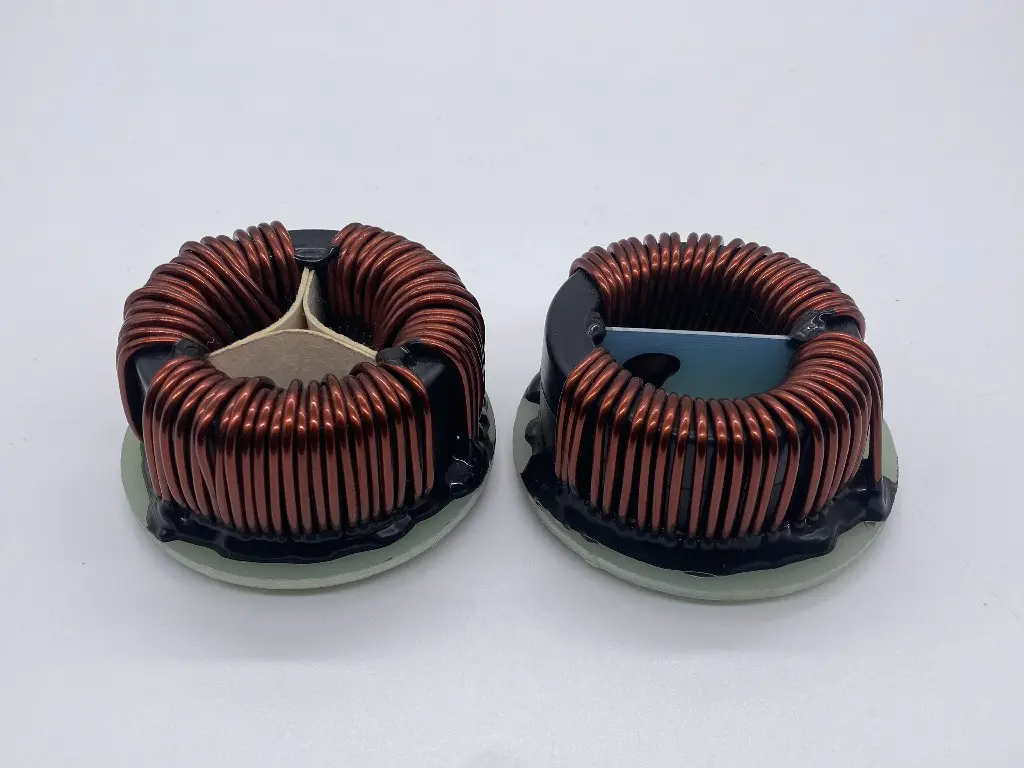
Transformers are widely used in various electric and electronic systems such as power systems, power supplies, telecommunications and audio systems, among others. The core is one of the most critical components in the transformer as it defines the transformer's performance. Amorphous toroidal cores have become a popular option for transformer manufacturers. This article looks at the advantages and limitations of using amorphous toroidal cores in transformers.
Advantages of Using Amorphous Toroidal Cores
Amorphous toroidal cores are made from iron-based alloys that are produced by cooling molten metal at a very high rate. The high cooling rate prevents the metal atoms from forming a regular crystalline structure, resulting in an amorphous or non-crystalline structure.
Higher Efficiency
One of the significant advantages of using amorphous toroidal cores in transformers lies in their improved efficiency. Amorphous cores typically exhibit lower eddy current losses than conventional laminated cores, which results in higher efficiency. Eddy current loss is a common problem in transformers where the magnetic field induces currents in the electrically conductive core material leading to energy losses.
The amorphous structure of the toroidal core helps to minimize eddy current loss by facilitating the free rotation of magnetic domains within the material. The resulting reduction in energy loss translates to significant energy savings, making amorphous toroidal cores an excellent option for green technologies.
Lower Noise
Another significant benefit of using amorphous toroidal cores is reduced noise. Transformers with conventional laminated cores often have a characteristic buzzing noise caused by the magnetostriction of the core material. This effect occurs because of the magnetization and demagnetization of the core material, resulting in microscopic changes in its shape and size. The amorphous structure of toroidal cores helps to minimize the magnetostriction effect and, as a result, reduces noise levels in transformers.
Reduced Core Losses
Amorphous toroidal cores also exhibit lower core losses than their laminated core counterparts. This is because the amorphous structure facilitates free rotation of magnetic domains, leading to less hysteresis loss. Hysteresis loss occurs due to the energy expended rearranging the magnetic domains in the core material as the magnetic field is transformed.
Laminated cores, on the other hand, have directional orientation, which reduces the free rotation of magnetic domains. The constrained movement of magnetic domains results in higher hysteresis loss and, as a result, higher core losses.
Improved Thermal Stability
The amorphous structure of toroidal cores also provides improved thermal stability over the laminated cores. The free rotation of magnetic domains allows the core material to dissipate heat better, leading to lower operating temperatures in transformers.
Limitations of Using Amorphous Toroidal Cores
Although amorphous toroidal cores offer numerous advantages, they also have some limitations that need to be considered.
Higher Cost
The most significant limitation of using amorphous toroidal cores is their higher cost. Since amorphous alloys are produced using a complex and expensive manufacturing process, amorphous toroidal cores are generally more expensive than laminated cores.
Limited Availability
Another limitation of amorphous toroidal cores is their limited availability. The manufacturing process is still in its early stages, with only a few manufacturers producing the material. This may cause supply chain issues and limit access to the material for transformer manufacturers.
Brittle Nature
Amorphous alloys also have a brittle nature that could result in cracking during the manufacturing or assembly stage. Manufacturers, therefore, need to be cautious during operation to prevent damage to the core.
Conclusion
Amorphous toroidal cores offer numerous advantages over conventional laminated cores, such as improved efficiency, reduced noise, lower core losses, and improved thermal stability. However, the higher cost, limited availability, and brittle nature of the material may restrict their use in the industry. It is, therefore, essential for transformer manufacturers to carefully consider the advantages and limitations of using amorphous toroidal cores before making a decision.